Carbon Neutrality Initiatives
To achieve carbon neutrality, the Mitsubishi Electric Group is working to reduce CO₂ emissions throughout the entire value chain. These efforts include improving energy efficiency in manufacturing processes, expanding the use of renewable energy, and enhancing the energy-saving performance of its products.
Product-Related Environmental Data Management – Leveraging the e-Pro System
To respond effectively to external requests for environmental data disclosure, the Mitsubishi Electric Group operates the e-Pro System, which centrally manages product-related environmental data—including power consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and material-specific weights of products and packaging. This system enables efficient collection, calculation, and disclosure of such data. The e-Pro System has helped the Group to visualize key challenges and promote eco-conscious design by enabling simplified calculations of LC-CO2* emissions based on annual energy consumption, destination markets, and product and packaging mass, as well as by facilitating feedback to design departments on targets related to carbon neutrality and the circular economy for specific product groups.
- Life Cycle CO2: All CO2 emissions throughout the entire life cycle of products and services
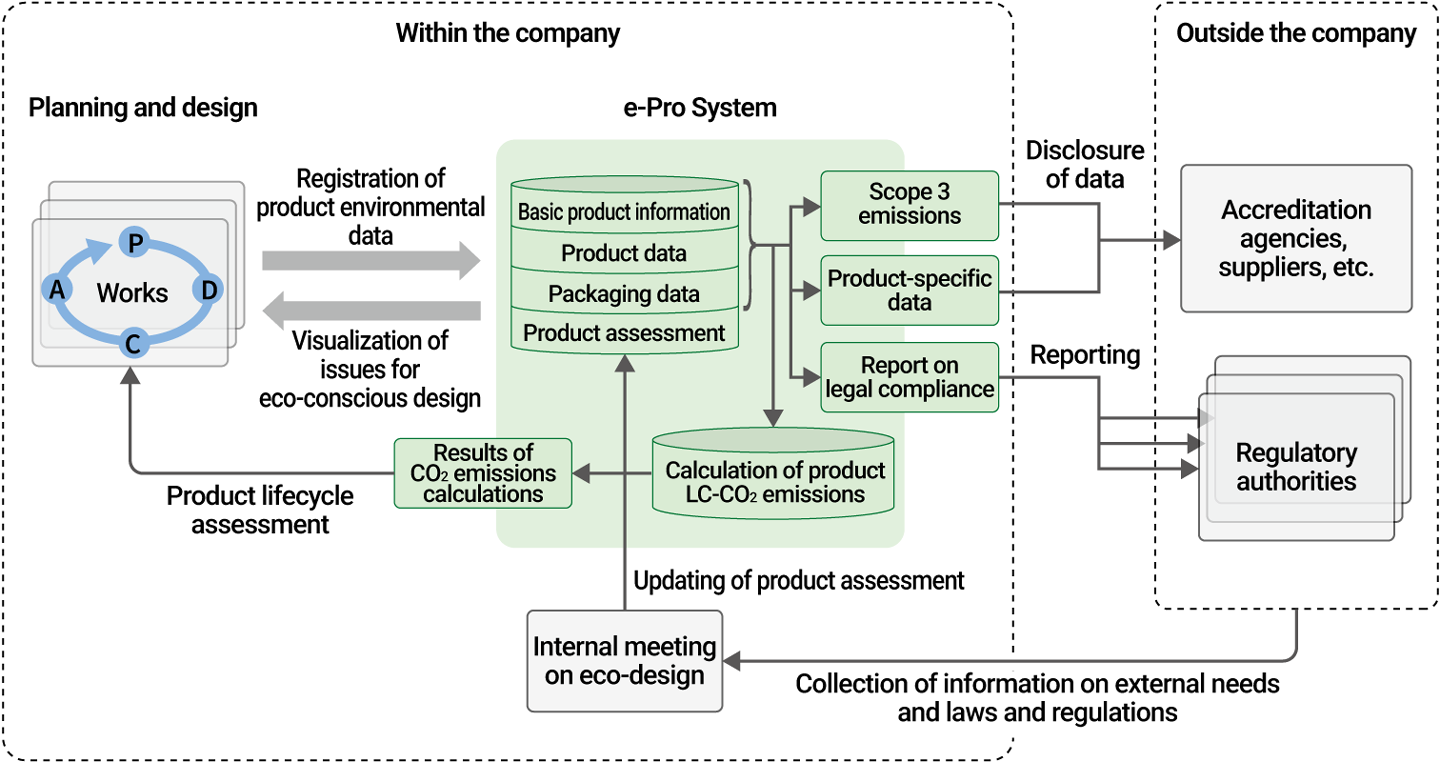
Overview of e-Pro System
CO2 Reduction Associated with Product Use
The Mitsubishi Electric Group is working to reduce CO2 emissions generated during product use (CO2 emissions equivalent to the amount of electricity consumed)—which far exceed those from production activities—by focusing on the following two approaches:
- Improving products to reduce CO2 emissions during use compared to previous models
- Enabling CO2 reductions through the use of products or their integration into other products
CO2 Reduction Through Product Improvement
To reduce CO2 emissions during product use compared to previous models through product improvement, the Mitsubishi Electric Group evaluates the degree of improvement in energy consumption for newly developed product models.
| Evaluation item | Product examples |
|---|---|
| CO2 Reduction Through Product Improvement | Monitoring, control, and protection devices for power generation plants and systems, railcar air-conditioning systems, electrical equipment for railcars, movable platform gates, vacuum circuit breakers, elevators, escalators, intelligent transport systems (ITS; ETC, smart interchanges), air conditioners, refrigerators, ventilation fans, electric fans, processing machines, LED light bulbs, residential lighting fixtures, turbine generators, optical communication network systems, wireless communication systems, and in-vehicle control devices |
CO2 Reduction Through Product Use or Integration
Some Mitsubishi Electric Group products contribute to reducing CO2 emissions at customer sites during use. For example, heat pump systems are expected to generate significantly lower CO2 emissions during operation compared to combustion-based heating and hot water systems. In addition, components such as inverters and power devices help improve the energy efficiency of the final products into which they are integrated, thereby contributing to CO2 emission reductions during use. To quantify this impact, the Group defines the difference in CO2 emissions between its products and potentially selected alternatives as its contribution to reducing CO2 emissions—and actively works to enhance it.
| Evaluation item | Product examples |
|---|---|
| CO2 Reduction Through Product Use or Integration | Water heating systems (heat pump electric water heaters, electric water heaters), inverters, power devices (power modules), total heat exchanging ventilation equipment, and electrical equipment for railcars (control devices) |
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Factories and Offices
The Mitsubishi Electric Group is working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from its factories and offices by targeting both energy-related CO2 and the non-energy-related GHGs emitted through its business activities—namely SF6, HFCs, and PFCs.
Reduction of Energy-Related CO2
To reduce energy-related CO2, the Mitsubishi Electric Group is promoting emission reduction through a range of initiatives, including:
- Planned installation and renewal of high-efficiency and energy-saving equipment and operational optimization
- Promotion of energy-saving initiatives during new building construction and facility renewal
- Knowledge sharing of energy-saving technologies for production equipment
- Promotion of electrification for equipment and vehicles, such as company cars and forklifts
- Procurement of renewable energy and non-fossil electricity, and adoption of power purchase agreements (PPAs)
Based on Japan’s Act on the Rational Use of Energy, 9 out of 20 specific Group companies in Japan, including Mitsubishi Electric, have been awarded as excellent business operators (S Class) in terms of energy saving.
Reduction of SF6, HFCs, and PFCs
Three types of non-CO2 greenhouse gases are emitted by the Mitsubishi Electric Group in its business activities: SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride), HFCs (hydrofluorocarbons), and PFCs (perfluorocarbons).
SF6 is used inside gas-insulated switchgear for electrical insulation, as well as in the etching process during semiconductor and liquid-crystal display production. HFCs are used as refrigerants in air conditioners and refrigerators, while PFCs are used during the etching process in production of semiconductors and liquid-crystal displays.
In fiscal 2025, emissions were reduced through continued efforts such as shifting to low-GWP refrigerants, improving operational practices, and recovering and destructing gases.
Expanding the Use of Renewable Energy
The Mitsubishi Electric Group is working to expand the use of renewable energy by identifying issues and evaluating the most suitable approaches for each region. These include installing photovoltaic power systems, exploring other renewable energy options, and utilizing renewable energy and non-fossil certificates. We are also examining the effective use of surplus solar power through self-wheeling.
Reducing CO2 Emissions from Logistics
The Mitsubishi Electric Group strives to improve transport efficiency and economy by visualizing logistics operations through quantitative evaluation and eliminating irrational, irregular and wasted efforts in operations, with the goal of realizing Economy & Ecology Logistics (Eco-Logistics) with little environmental impact.
In Japan, the Mitsubishi Electric Group is continuously working to reduce CO2 emissions through the following measures:
- Reviewing transportation routes
- Switching from truck transportation to rail transportation (modal shift)
- Reducing the number of trucks by improving load ratios (including Container Round Use)
Overseas, the Group is also pursuing optimal logistics tailored to the specific conditions of each country.
Climate Change Initiatives (TCFD-Based Disclosure)
The Mitsubishi Electric Group has expressed its support for the recommendations of the TCFD, and as such, the Group promotes efforts and discloses information in line with these recommendations.
