Initiatives toward a Circular Economy
The Mitsubishi Electric Group is actively engaged in the circular economy, undertaking initiatives such as recycling plastics and reducing water usage to mitigate environmental impacts.
Effective Utilization of Plastic Waste
Based on Japan’s Resource Circulation Strategy for Plastics, the Mitsubishi Electric Group is prioritizing the effective utilization of plastic waste* and has established a medium-term target of achieving 100% effective utilization of plastic waste by fiscal 2036.
In Japan, the Group manages the volume of plastic waste generated at its production sites, enforces rigorous sorting, and continually reviews and selects waste-processing contractors. Looking ahead, we will further suppress plastic waste output by sharing contractor information among production sites and promoting the visualization of plastic waste. We also plan to improve the material-recycling ratio of plastic waste.
Overseas, where laws, regulations, and waste-treatment systems vary by country and region, the Group strives to understand actual waste generation and recycling rates, set targets tailored to each locale, and implement targeted initiatives to meet those goals.
- Waste refers to items that are no longer needed at a site. This includes items that have been disposed of directly, entrusted to a third party for disposal, or sold/transferred to others.
Generating High-Purity Plastics from End-of-Life Home Appliances
The Mitsubishi Electric Group employs proprietary technology to convert end-of-life home appliances into high-purity plastics. Insights obtained during this recycling process are fed back into product design, driving continuous improvements in product recyclability rates.
Mitsubishi Electric Group’s Proprietary Technology for Producing High-Purity Plastic from Home Appliances
|
Closed-Loop Recycling of Plastic
The Mitsubishi Electric Group is advancing closed-loop recycling in which high-purity recycled plastics produced within the Group are reused in Mitsubishi Electric home appliances.
For example, we have developed a technology that produces regenerated PC/ABS* with consistent quality, high durability, and flame retardancy by utilizing PC/ABS recycled from end-of-life appliances. This regenerated material is used in wireless communication terminals for sensor applications, such as gas meter reading systems. This has enabled reductions of approximately 70% in the volume of new plastic used in these components and 57% in CO2 emissions compared to manufacturing PC/ABS from new raw materials. In addition, we are working to expand the use of recycled plastics to other applications, such as plastic boxes for wire EDM machines and home appliances.
- A plastic which is a blend of polycarbonate (PC) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
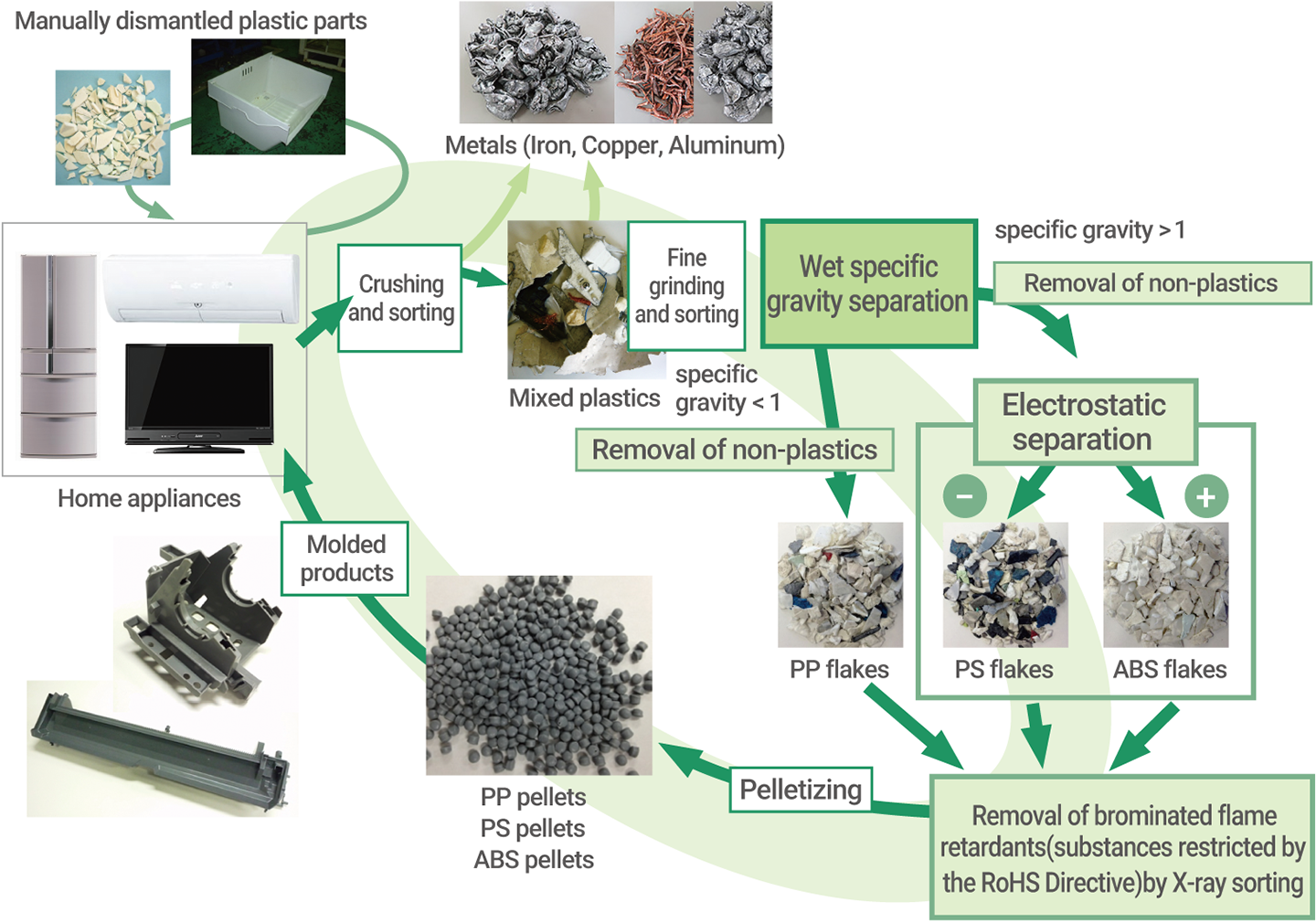
Flow chart of Mitsubishi Electric Group closed-loop plastic recycling
Creating a Service in the Recycling Business
Leveraging technology cultivated in the home appliance recycling business, the Mitsubishi Electric Group plans to offer its Smart Plastic Separation DX Solution RaaS* to enable utilization of its advanced plastics separation technology using static electricity (electrostatic separation) in the plastics recycling of customers.
The RaaS solution uses sensors to collect data on factors that affect electrostatic separation (raw material composition, input volume, etc., of the shredded plastics mixture) and the results of separation, which is then analyzed using AI to automatically control the position of partitions and the voltage in the receptacles that collect the separated plastic. Such use of digital and smart technologies in electrostatic separation makes it possible to separate a variety of mixed plastics in a stable manner, thereby contributing to the production of high-quality recycled plastics. The Mitsubishi Electric Group will expand the circle of resource circulation with the aim of realizing a circular economy by offering the RaaS solution to customers in a variety of industries beyond the home appliance industry.
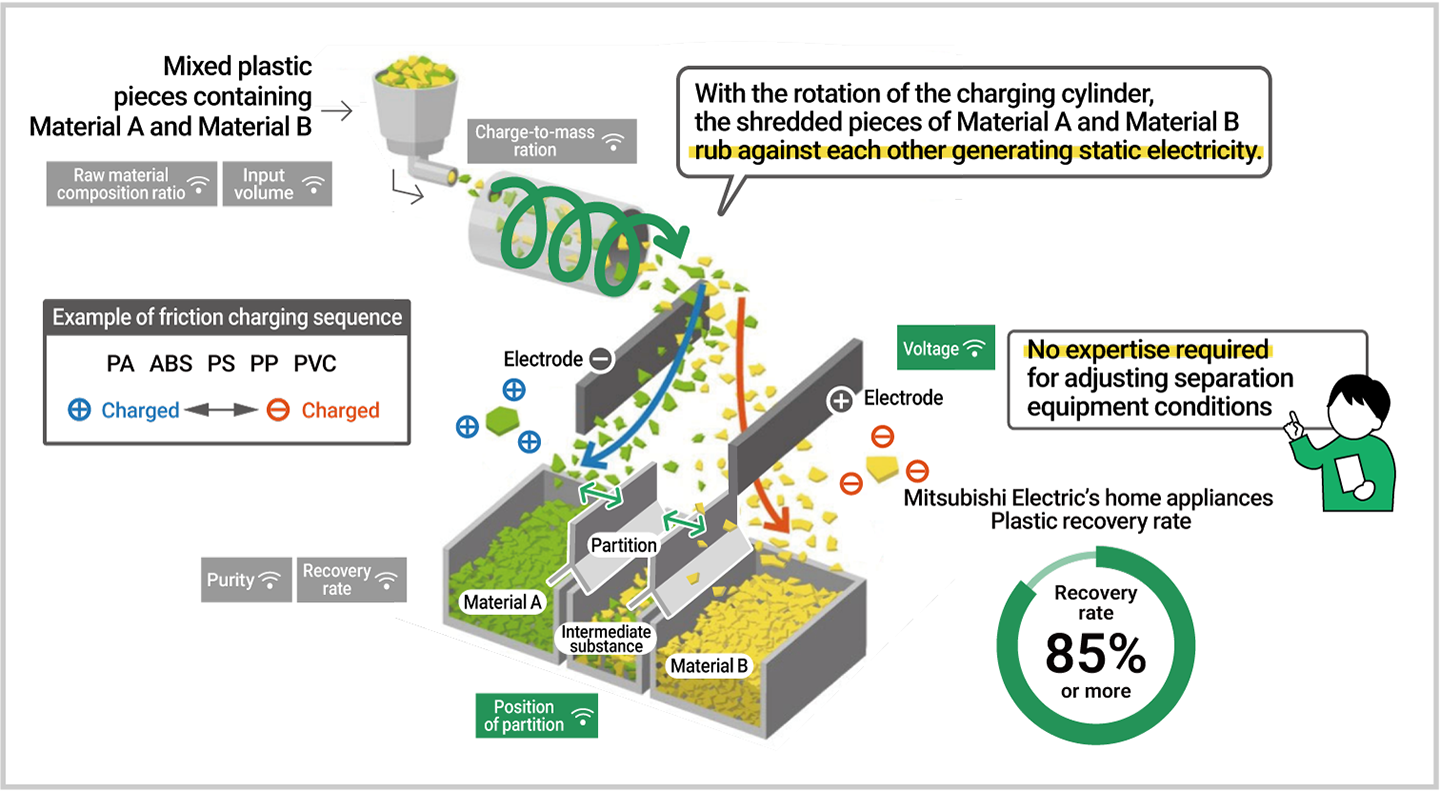
Smart Plastic Separation DX Solution RaaS
- Recycle as a Service
3Rs for Packaging Materials
The Mitsubishi Electric Group is advancing the 3Rs—Reduce, Reuse, Recycle—of the packaging materials required for product transportation, with the goal of minimizing overall packaging use.
<3Rs for Packaging Materials>
- Reduce : simplify packaging designs to use fewer materials
- Reuse : broaden the application of returnable containers and packaging
- Recycle : reclaim and reprocess used packaging materials
Reducing Water Usage
Managing Water Risk
Globally, escalating water shortages, pollution, and climate-change-driven extreme weather are severely impacting raw-material sourcing and product manufacturing, underscoring the critical importance of corporate water-risk management.
The Mitsubishi Electric Group evaluates water stress and quality at approximately 160 manufacturing sites—including associated companies—using Aqueduct*1 and Water Risk Filter.*2 We also assess species-extinction risk with the IBAT*3 (STARt). By combining these results with each site’s operational profile (business scope, production-related water use, etc.), we have quantified the water risk at every production location. We will consider setting water-related targets for high-risk sites, taking into account the circumstances of their watershed. We also work to minimize local environmental impacts by complying with regional wastewater standards and, during product development, assessing effects on water sources and conducting lifecycle evaluations to reduce overall environmental burden.
- 1 Water risk assessment tool developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI), used to assess “baseline water stress” and “coastal eutrophication potential.”
- 2 Water risk analysis tool developed and operated by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), used to assess “baseline water stress,” “blue-water scarcity,” and “surface water quality index (BOD).”
- 3 Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool: The assessment is based on the threat abatement (t) component of the Species Threat Abatement and Restoration Metric (STAR)
Response to High-Risk Sites
Conceptual diagram of water risk analysis
The Mitsubishi Electric Group has identified five production sites* as high-risk sites based on Aqueduct water-risk evaluations and each site’s operational profile, and actively manages their water risk. Under our Environmental Plan 2025, we have set a target to reduce water consumption per unit of sales at these high-risk sites by at least 6% in fiscal 2026 versus fiscal 2020. To achieve this, we are monitoring water-saving performance in water-using equipment, tracking rates of water reuse, installing and utilizing low-flow faucets, and taking other water-saving measures.
We will continue to co-exist in harmony with local communities by implementing effective water risk measures in consideration of regional characteristics and circumstances at each production site, with a focus on high-risk sites.
- The following manufacturing companies located in Thailand:
- Mitsubishi Electric Consumer Products (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
- Siam Compressor Industry Co., Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Automation (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Elevator Asia Co., Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Thai Auto-Parts Co., Ltd.
Status of Water Usage, Intake, Drainage, and Reuse
The Mitsubishi Electric Group treats water used in production processes and reuses it in those same processes, and repurposes purified wastewater for toilet flushing, cooling towers, etc. The Group also reduces groundwater consumption by harvesting rainwater.
At its production sites, water is taken to be used mainly for cooling, cleaning and adjusting the concentration of water-based paints, and as a solvent, an additive to materials and a heat medium. Each site regulates wastewater discharge according to its voluntary effluent-quality standards to ensure compliance with local statutory limits. When applicable, these standards also integrate local discharge criteria aligned with the receiving water body’s characteristics.
