History
1920s-1970s
1970s
- Released a petroleum gas fan heater and FF-type petroleum gas storage hot water supply equipment. (1978)
- Installed elevators which traveled 600 meters per minute, the fastest in the world at that time. (1978)
- Released a futon drier, the RO-1500 range oven, and an electronic heated table (kotatsu) model. (1977)
- Launched the ETS-II engineering test satellite, the first in a series of ETSs for which Mitsubishi Electric was the prime contractor. (1977)
- Produced Japan's largest-capacity nuclear power generator (1,300,000kVA) and a full gas-insulated substation (550kV). (1976)
- Participated in national ultra-LSI R&D project aimed at "Studying Large-Scale Integrated Circuit Technology for the Next Generation of Digital Computers." (1976)
- Introduced a large general-purpose computer, MELCOM COSMO 700. (1974)
- Released the MELSEC310 sequencer. (1972)
- Launched MOLDIS (Mitsubishi Online Distribution Information System) - Japan's first full-scale online realtime distribution information system. (1972)
- Completed the 560,000 kVA turbine generator -- Japan's largest -- for the Kansai Electric Power Company's Mihama Power Plant. (1970)
- Introduced the LOSSNAY heat-exchange ventilation system. (1970)
1960s

1967
Earth-station antenna
- Released the best-selling MELCOM83 small business computer. (1969)
- Developed the world's first permanent fuse. (1969)
- Chosen as the prime contractor for Japan's first working satellite for ionosphere sounding. (1969)
- Adopted "ADVANCED AND EVER ADVANCING" as our corporate slogan. (1969)
- Released a wall-mounted split-system room air conditioner featuring a line flow fan. (1968)
- Completed the first Mitsubishi nuclear power generator (400,000kVA). (1968)
- Delivered an earth-station antenna to the Mexican Ministry of Communication for use with an international satellite. (1967)
- Began technological cooperation on space technology with America's TRW. (1966)
- Manufactured a commercial CVCF inverter and developed a VVVF inverter. (1965)
- Supplied radar equipment to the weather station atop Mt. Fuji. (1964)
- Delivered 1650 kVA main transformer and 185 kW electric motor for use in the Shinkansen (Bullet Train). (1963)
- Delivered Japan's first subway train with an automatic train-operation (ATO) system. (1962)
- Released Japan's first IC chip: the Molectron. (1961)
- Produced the first Mitsubishi color TV, incorporating technology developed by RCA Corp. (1960)
- Launched Mitsubishi Electric's initial computer entry, MELCOM 1101. (1960)
1950s

The first Mitsubishi Electric television (Model 101K-17), launched in 1953.
- Completed the first Mitsubishi electrical-discharge machine. (1958)
- Completed 105,000 kVA Francis-type hydraulic turbine generator for the J-Power Tagokura power plant, featuring umbrella-type construction with Japan's highest generation capacity. (1957)
- Completed the ITV - Japan's first ever industrial use television. (1954)
- Released the first Mitsubishi Electric television (Model 101K-17). (1953)
- Completed Japan's first DD50 diesel-electric locomotive, for the Japan National Railways. (1953)
- Began semiconductor research. (1952)
- Succeeded in making Japan's first V-type oil circuit breakers for use on ultra high-voltage lines (287.5kV/5,000MVA). (1951)
1940s
- Commenced production of radios and speakers. (1945)
1930s
- Installed the first Mitsubishi electric power generation equipment. (1938)
- Listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. (1937)
- Delivered the first Mitsubishi elevator. (1935)
- Delivered the first Mitsubishi escalator. (1935)
- Marketed no-fuse breakers, the first domestically produced fuseless circuit breakers (15-35 amperes). (1933)
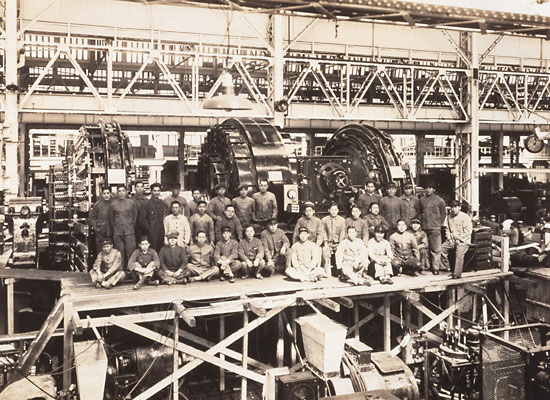
Factory in the 1930s. Commemorating the completion of Japan's largest (at the time) motor with an output of 9000 hp.
1920s

1924 Vertical-axle
hydraulic generator
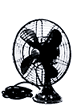
1921-23 Electric fan
- Completed the first domestically produced railway substation, for the Odawara Kyuko Railway. (1928)
- Produced the first Mitsubishi vertical-axle hydraulic generator (2,300kVA). (1924)
- Technological licensing agreement signed with Westinghouse Electric International. (1923)
- Manufactured approximately 10,000 electric fans. (1921-1923)
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation established with paid-in capital of 15 million yen. (1921)
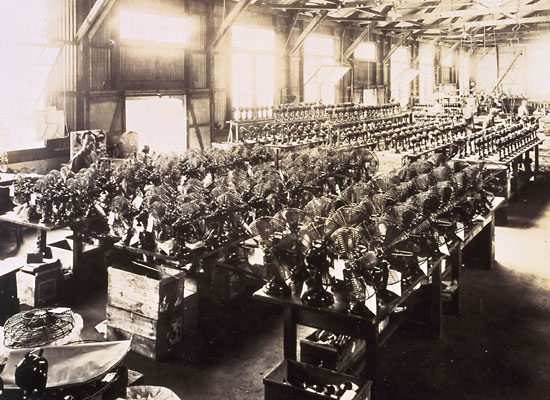

Mitsubishi Electric's first mass-produced consumer product. Mitsubishi Electric's technical expertise in heavy electric systems was applied to manufacture products for the home.
